The Sumerians, one of the earliest civilizations in human history, established a complex societal structure that played a critical role in their day-to-day life and governance. Their social classes were delineated by various factors, including wealth, occupation, and lineage, creating a hierarchy that influenced everything from politics to personal relationships. The Sumerians thrived in the fertile region of Mesopotamia, where their social stratification helped them manage resources and organize labor to build remarkable cities and advancements in agriculture, trade, and writing.
In examining the Sumerians social classes, we find a diverse array of roles and responsibilities that helped maintain order and stability in their communities. From the ruling elites who held power to the farmers and laborers who sustained the economy, each class had its place in the grand tapestry of Sumerian life. Understanding these classes not only provides insight into the Sumerians' daily existence but also highlights the complexities of human societies as they evolved over time.
As we delve deeper into the topic, we will explore the varying tiers within Sumerian society, the roles and responsibilities of each class, and how these social structures influenced the culture and innovations of the time. The Sumerians social classes were not just mere labels; they were foundational elements that shaped the lives and legacies of one of history's greatest civilizations.
What Were the Main Social Classes of the Sumerians?
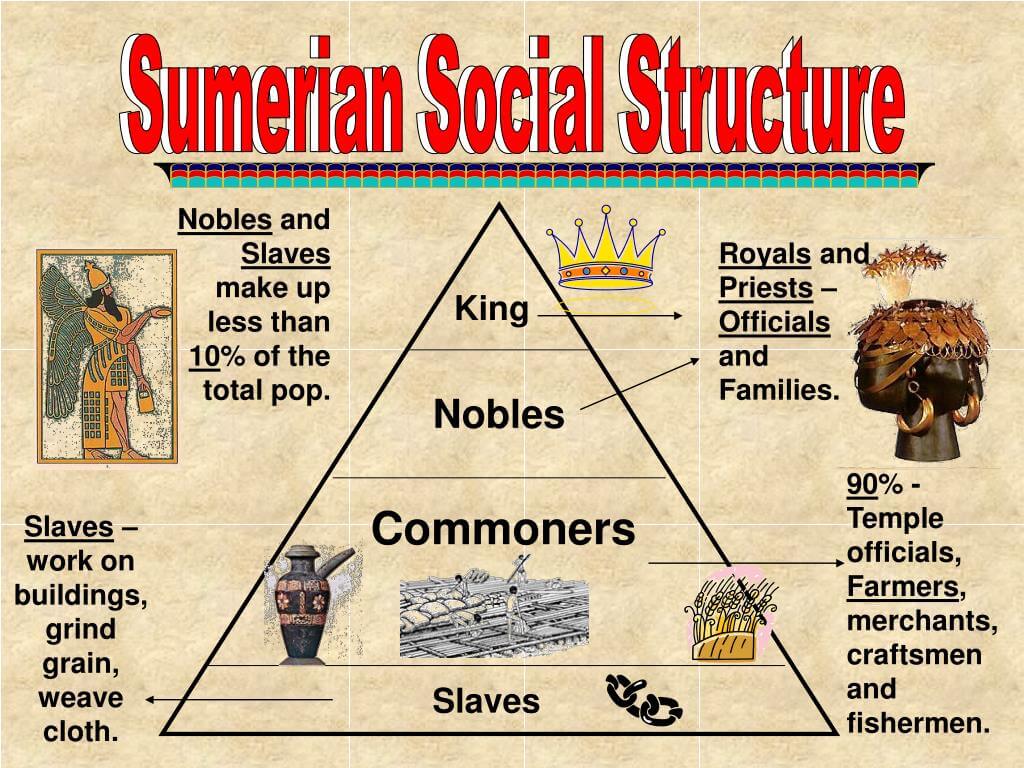
The Sumerian social structure was primarily divided into four main classes:
- Nobility: This class consisted of kings, priests, and high officials.
- Commoners: Comprised of farmers, artisans, and merchants.
- Clients: Individuals who depended on the nobility for protection and resources.
- Slaves: The lowest class, often captured in wars or born into slavery.
How Did the Nobility Influence Sumerian Society?
The nobility held significant power in Sumerian society, influencing everything from lawmaking to religious practices. These individuals were often landowners, and their wealth allowed them to exert control over the lower classes.
What Role Did Priests Play in Sumerian Social Classes?
Priests were a vital part of the nobility, serving as intermediaries between the gods and the people. They managed temples, conducted religious ceremonies, and oversaw agricultural festivals, thereby enhancing their influence over both spiritual and economic aspects of life.
How Did Commoners Contribute to Sumerian Society?
Commoners played an essential role in sustaining the economy. Farmers cultivated crops, while artisans produced goods and merchants facilitated trade. This class formed the backbone of Sumerian society, supporting the upper classes through their labor.
What Challenges Did Commoners Face?
Despite their crucial contributions, commoners often faced numerous challenges, including:
- Poor living conditions due to limited resources.
- Heavy taxation imposed by the ruling elite.
- Vulnerability to droughts and floods that threatened their livelihoods.
What Was the Status of Clients in Sumerian Society?
Clients occupied a unique position within the Sumerians social classes. They were typically free individuals who had a patron from the nobility, relying on them for protection and support in exchange for labor and loyalty.
How Were Slaves Treated in Sumerian Society?
Slavery in Sumerian society was often a result of war or debt. Slaves had no rights and were viewed as property. Their treatment varied depending on their masters, but many worked in harsh conditions, particularly in agriculture and construction.
Did Social Mobility Exist Among the Sumerians?
While the Sumerians social classes were rigid, instances of social mobility did occur. Some commoners could improve their status through:
- Successful trade ventures.
- Marriage into a higher class.
- Exceptional skills or talents that garnered recognition.
How Did the Sumerians Social Classes Influence Culture and Innovation?
The stratification of Sumerian society had profound implications for their culture and innovations. The wealth generated from agriculture and trade allowed for advancements in:
- Writing systems, including cuneiform.
- Architecture, evident in the construction of ziggurats.
- Mathematics and astronomy, leading to the development of the calendar.
Conclusion: The Legacy of Sumerians Social Classes
The Sumerians social classes were more than just a hierarchy; they were integral to the functioning and development of one of the earliest civilizations in human history. By understanding these classes, we can appreciate the complexities of Sumerian life and the contributions they made to future societies. Their social structure shaped not only their culture but also the pathways for future civilizations, leaving a lasting legacy that continues to influence our understanding of social organization today.
You Might Also Like
Is Harry Styles Wearing A Toupee? The Truth Behind His HairstylesBehind The Scenes: The Impact Of Dan Bongino’s Producer Joe
Discovering The Best Viewer For Second Life In 2024
Unveiling The Truth: Is Kamala Harris An Alcoholic?
Embracing The Dawn: Morning Prayers To Start The Day
Article Recommendations
- Gal Gadot Dan P Diddy
- Val Kilmer Topgun
- King Von Autopsy
- Jessica Alba
- Who Is Morgan Freemans Partner
- Katherine Harbaugh
- P Diddy Kim Kardashian Video
- Karrueche
- Steve Liam Payne Manager
- Wentworth Miller Husband